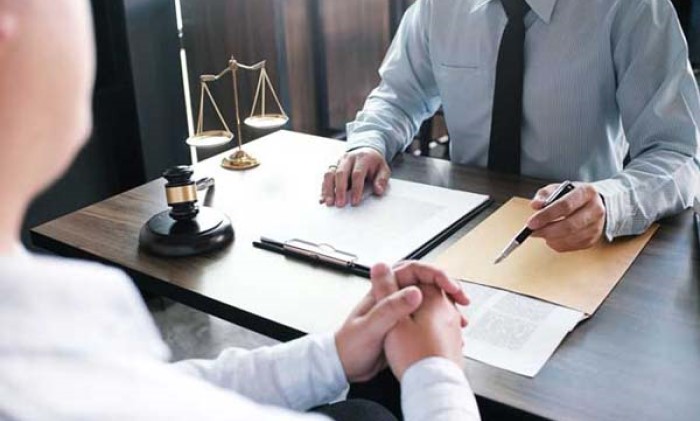
Introduction
Workplace safety is paramount for both employers and employees. However, accidents can still occur, sometimes involving third parties beyond the employer-employee relationship. Understanding third-party liability for workplace accidents is crucial for ensuring proper compensation and legal recourse. In this detailed guide, we explore the intricacies of third-party liability, covering everything from its definition to legal considerations and practical implications.
Understanding Workplace Accidents
Defining Workplace Accidents
Workplace accidents encompass any unforeseen incidents that occur within a work environment, resulting in injury, illness, or property damage. These incidents can range from slips and falls to machinery malfunctions and chemical exposures.
Statistics on Workplace Accidents
Before delving into third-party liability, it’s essential to grasp the prevalence of workplace accidents. According to recent data from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), millions of workplace injuries occur annually in the United States alone, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive safety measures.
Exploring Third-Party Liability
What is Third-Party Liability?
Third-party liability refers to the legal responsibility of entities or individuals outside of the employer-employee relationship for workplace accidents. This liability can arise when a third party’s actions or negligence contribute to an employee’s injury or harm.
Types of Third Parties
Identifying potential third parties is crucial for determining liability in workplace accidents. These parties may include contractors, subcontractors, vendors, customers, or even bystanders who are not directly employed by the victim’s company but interact with the workplace environment.
Legal Framework and Considerations
Legal Principles Governing Third-Party Liability
Understanding the legal principles governing third-party liability is essential for navigating related claims effectively. Common legal theories include negligence, premises liability, product liability, and vicarious liability.
Comparative Negligence in Third-Party Claims
In cases where both the employer and a third party share responsibility for an accident, the concept of comparative negligence comes into play. This principle allows courts to assess each party’s degree of fault and allocate liability accordingly.
Key Factors in Establishing Liability
Proving Causation and Negligence
Establishing third-party liability requires demonstrating that the third party breached a duty of care owed to the injured party and that this breach directly caused the accident or injury. Evidence such as eyewitness testimonies, documentation, and expert opinions play a crucial role in substantiating these claims.
Contractual Agreements and Indemnification
Reviewing contractual agreements is essential, as they may contain indemnification clauses that outline each party’s responsibilities and liabilities in the event of an accident. Understanding these provisions is crucial for determining the extent of third-party liability.
Practical Implications and Risk Mitigation
Importance of Comprehensive Insurance Coverage
Maintaining adequate insurance coverage, including general liability and workers’ compensation insurance, is vital for mitigating the financial risks associated with third-party liability. Employers should review their policies regularly to ensure sufficient protection.
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
Prevention is always better than cure. Employers should prioritize workplace safety through robust risk management strategies, including regular safety training, equipment maintenance, and hazard assessments. By fostering a culture of safety, companies can minimize the likelihood of accidents and potential third-party liability claims.
Case Studies and Examples
Landmark Cases in Third-Party Liability
Examining real-life examples of third-party liability cases provides valuable insights into the legal precedents and complexities involved. From construction site accidents to product defects, these cases highlight the diverse nature of third-party liability scenarios and the importance of diligent legal representation.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Drawing lessons from past cases, employers can identify best practices for preventing workplace accidents and mitigating third-party liability risks. Whether through improved oversight, contractual clarity, or collaborative safety initiatives, there are numerous strategies for enhancing workplace safety and protecting against liability.
FAQ Section
1. What qualifies as a third-party in workplace accidents? Third parties in workplace accidents can include contractors, subcontractors, vendors, customers, or any external entities not directly employed by the victim’s company.
2. How does comparative negligence apply to third-party liability claims? Comparative negligence allows courts to assess each party’s degree of fault in an accident and allocate liability accordingly, even when both the employer and a third party share responsibility.
3. What role do indemnification clauses play in third-party liability cases? Indemnification clauses in contractual agreements outline each party’s responsibilities and liabilities in the event of an accident, impacting the extent of third-party liability.
4. What are some practical steps employers can take to mitigate third-party liability risks? Employers can mitigate third-party liability risks by maintaining comprehensive insurance coverage, implementing robust risk management strategies, and prioritizing workplace safety through training and hazard assessments.
5. Can you provide examples of landmark cases involving third-party liability for workplace accidents? Landmark cases involving third-party liability span various industries and scenarios, highlighting the diverse nature of liability claims and the importance of legal diligence.
6. How can employers learn from past cases to improve workplace safety and liability management? By studying past cases and identifying best practices, employers can enhance workplace safety measures, minimize accident risks, and effectively manage third-party liability exposure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, third-party liability for workplace accidents is a multifaceted issue with significant legal, financial, and practical implications. By understanding the complexities of third-party liability, employers can better protect their employees, mitigate risks, and foster safer work environments. Through diligent risk management, adherence to legal principles, and continuous improvement, companies can navigate third-party liability challenges with confidence and resilience.